 Courtesy:
Courtesy:
Conversations on forced displacement in many cases still centre on the climate versus conflict dichotomy, but multiple factors including social inequality, poor infrastructure and weak governance, often combine as triggers for displacement. A more analytical approach to financing forced displacement response is necessary to enable humanitarian actors to work more effectively in the allocation of resource and disaster preparedness.
 Courtesy:
Courtesy:
Gateway House presents a timeline that highlights the cross-border dynamics between Myanmar and India’s northeast. Myanmar’s military coup and breakdown of authority have aggravated existing local problems related to population displacement, border security, competition for resources and ethnic tensions. Now India must engage more directly with the entities that control land along its borders, and the local communities who know it best.
 Courtesy:
Courtesy:
The timeline records the daily instances and ongoing cross-border dynamics between India and Myanmar since the February 2021 military coup in Myanmar. It tracks the events taking place in the eight states along the Indo-Myanmar border—four states in India (Arunachal Pradesh, Nagaland, Mizoram, and Manipur) and four in Myanmar (Kachin, Sagaing, Chin, and Rakhine), revealing their social, political and economic interconnectedness.
 Courtesy:
Courtesy:
Digital ecosystems, their evolution and regulation was the focus of USAID’s annual conference on global digital development. For Global South actors, the conference offered suggestions on addressing climate impact, disinformation, and building resilient digital infrastructure.
 Courtesy: Purvi Patel
Courtesy: Purvi Patel
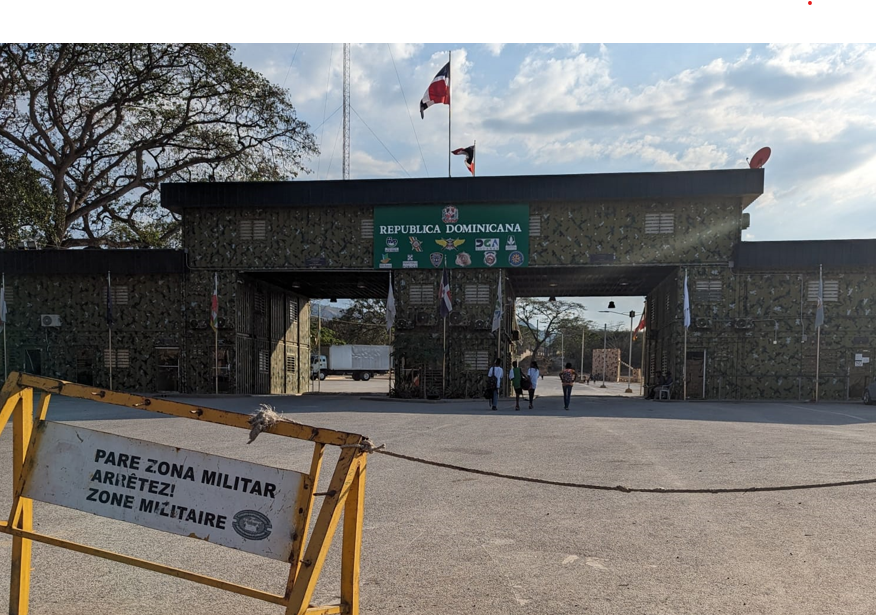
How can hyper-local, cross-border dialogue provide stability in border communities? International Affairs Fellow at the Council on Foreign Relations and Visiting Fellow at Gateway House, Purvi Patel, on a recent visit to Haiti and the Dominican Republic, observed similarities with other complex cases such as the India-Myanmar border and offers lessons for them.
 Courtesy: Reuters
Courtesy: Reuters
In March, the U.S. announced an extension of Myanmar’s Temporary Protected Status (TPS), in light of the deteriorating situation. TPS provides legal status in the U.S., as an alternative to refugee status, to all nationals of a designated country fleeing instability. TPS shares similarities and key differences with refugee status, which are worth understanding in order to build strong protective legal framework for forcibly displaced communities.
 Courtesy: India Today
Courtesy: India Today
Former President Trump and incumbent President Biden have emerged as frontrunners in the ongoing U.S. primaries. While the former faces several legal hurdles, the latter has been criticised for his response to the crises in Israel and Ukraine and the strategic contest with China. Neelam Deo, co-founder, Gateway House, speaks with Purvi Patel, International Affairs Fellow, Council on Foreign Relations, about the electoral race, legal challenges to Trump's candidature, and what India can expect from another Trump presidency.
 Courtesy: Bloomberg
Courtesy: Bloomberg
Two climate and environment conferences in December 2023, one with global attention in Dubai and the other with a hyper-local focus in the Eastern Himalayas, highlighted the need for a more nuanced conversation on climate and forced population displacement. They both point to a need for a multi-factored model in the analytical approach to forced migration.
 Courtesy: Revolutionary Communist Group
Courtesy: Revolutionary Communist Group
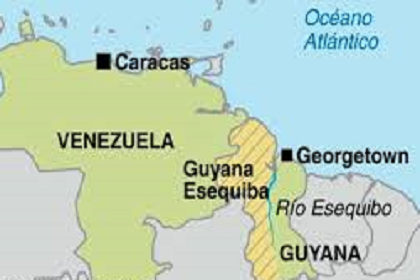
Venezuela's claim to the Essequibo region of neighbouring Guyana has focused world attention on yet another colonial-era border dispute. With elections coming up, the declining Venezuelan economy laying claim to newly-discovered rich oil and mineral deposits in Guyana has some traction. For Guyana, the claim to its land is non-negotiable as this developing country looks forward to accessing its own wealth. Purvi Patel, Visiting Fellow at Gateway House and Latin America expert, offers her insight.
 Courtesy: Scroll
Courtesy: Scroll
From COP to COP, the discussions focus on climate change and its impacts. But none have yet addressed a critical issue: the definition of a “climate refugee” or climate-related forced migration. Some contend that the issue requires a revision in the 1951 Refugee Convention. But with refugee and migrant flows to the borders of Western democracies, the term “refugee” is often re-framed as a concern about preservation of culture and values.











