 Courtesy: Symbior Solar
Courtesy: Symbior Solar
While several Bay of Bengal countries are rich in hydropower and thermal electricity generation, others are net energy importers with large markets. India can lead creative energy projects with its eastern neighbours, supported by regional and international institutions.
 Courtesy: Institute of Peace and Conflict Studies
Courtesy: Institute of Peace and Conflict Studies
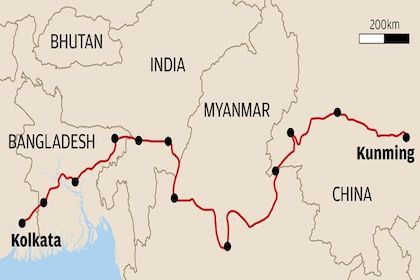
China is a clear winner in the physical connectivity stakes in the Bay of Bengal, and there's a reason a why: Its projects are connected to one another, from rail to road to port. While India also has some successful cross-border road and rail infrastructure projects, they are often an extension of an existing railway line or highway, not specific to the connectivity needs of the region. India can win by focussing instead on building infrastructure to maximise the vast maritime potential of the Bay of Bengal, especially the Andaman and Nicobar Islands that give India access to critical sea channels and trade routes.
 Courtesy: Gateway House
Courtesy: Gateway House
The Bay of Bengal is a bridge between the Indo-Pacific and the Indian Ocean, and with a population of 1.4 billion, an increasingly important economic zone in its own right. India has been slow to build regional connectivity. The space has been filled by China's Belt and Road Initiative projects, which have not always been beneficial for host countries. The region may be better off pursuing digital connectivity by enabling tech startups – areas of India’s strength. This research uses maps to explore the potential for energy, transport, and financial connectivity across the Bay of Bengal.
 Courtesy: www.aithority.com
Courtesy: www.aithority.com
Altizon’s product uses machine data to help better business decision-making for its overseas manufacturing customer base. It particularly improves productivity, power and utilities consumption and predictive maintenance. Altizon is now in the prestigious Gartner Magic Quadrant, one of only 16 globally-recognised niche players for Industrial IoT platforms. It is getting attention from Indian SMEs.
 Courtesy: BITS Pilani
Courtesy: BITS Pilani
In June 2019, BITS Pilani became the first academic institution, globally, to offer a Master’s programme in Digital Manufacturing. The programme, currently open only to working professionals, focuses on developing an expertise in the manufacturing of the future including Industrial IoT, additive manufacturing, big data analytics, industrial cybersecurity, and logistics and supply chain optimisation. The ongoing pandemic has exponentially increased digital adoption, increasing the demand for the study of digital manufacturing within corporate India.
 Courtesy: ClairViz
Courtesy: ClairViz
ClairViz offers products and services that help manufacturing companies digitally transform their factory floor. It uses its project engineering, design, electrical, automation and software skills to transform them into modern, data-driven facilities. This start-up smartly benefits from government programmes: housed in a state-supported incubator, clients are public sector enterprises mandated to use small and medium entrepreneurs in their supply chains.
 Courtesy: Charles Platiau/Reuters
Courtesy: Charles Platiau/Reuters
Schneider Electric’s domain expertise in hardware and software has helped it create a proprietary and comprehensive suite of Industry 4.0 solutions. The company is now deploying these in all of its eight manufacturing facilities spread across India with favourable results: 30% reduction in energy costs, 10% improvement in mean time to repair and 5% improvement in logistics. Schneider intends to make these Lighthouse network facilities, thereby setting the standard for other manufacturing MNCs in India.
 Courtesy: LinkedIn | Drishti
Courtesy: LinkedIn | Drishti
Using computer vision and AI to capture factory-wide data of human operators, Drishti Technologies co-relates human actions to line efficiencies, bottlenecks and root-cause analysis. Indian manufacturers operating at the lower end of the automation curve can use this combination to improve productivity, safety and quality by a deep-dive into human-action analytics.
 Courtesy: C4i4
Courtesy: C4i4
C4i4 is a part of the Government of India's Samarth Udyog initiative, and aims to hand-hold micro, small and medium enterprises (MSMEs) in the journey towards digitisation. Though MSMEs account for 45% of manufacturing output and 40% of exports, almost 90% of them lack access to markets beyond their limited geography. C4i4 helps them scale productivity and quality, and compete in global markets.
 Courtesy: Twitter|@SiemensIndia
Courtesy: Twitter|@SiemensIndia
The 50-year-old Siemens facility in Kalwa adopted the Internet of Things, cloud and digital twin technologies to transform itself digitally and optimise manufacturing processes. It led to a 20% increase in productivity, and has made its product competitive with its German counterpart.












