 Courtesy: Oxford University Press
Courtesy: Oxford University Press

Sifra Lentin
Bombay History Fellow
Sifra Lentin is Fellow, Bombay History Studies. She was Visiting Fellow 2018 at the Herbert Katz Center for Advanced Judaic Studies at University of Pennsylvania for a project on Karachi’s Jews. Her latest Gateway House policy report on “India and the SCO, Bound by Buddhism” (November 2020) proposed how India could leverage her soft power as the holy land of Buddhism in this multilateral grouping. Her “Mumbai-Shanghai Sister Cities” report (May 2017): proposed recommendations on how sister city relationships between these two cities can be made to work. She has also written a number of books, namely, Bombay’s International Linkages (Gateway House, 2019); Our Legacy: The Dwarkadas Family of Bombay (2018), and A Salute to the Sword Arm – A photo Essay on the Western Fleet (Western Naval Command, 2007). Her work has also appeared in edited volumes: “The Jewish Presence in Bombay” in India’s Jewish Heritage: Ritual, Art, & Life-Cycle (Marg Publication, 2002), “Shalom India” published in One India One People’s book Know India Better (2006), “The Jewish presence in Mumbai: their contribution to the city’s economic, social and cultural fabric”, in Mumbai—Socio-Cultural Perspectives: Contribution of Ethnic Groups & Communities (Primus Books, 2017).
Sifra graduated in English Literature from Elphinstone College, Mumbai, and went on to complete her Bachelor’s in General Law (BGL) from Government Law College, Mumbai. Her earlier career was in journalism with a focus on Bombay and South Asian Jewish history. Most notably, she wrote a popular thrice-weekly column for Mid-Day “Vintage Mumbai” from 1995 to 1997 and a five-part Partition series for Reuters on the golden jubilee of Indian Independence in 1997. She is on the Board of Trustees of the Sir Jacob Sassoon School (Byculla, Mumbai).
History, Bombay
Recent projects
 Courtesy: Oxford University Press
Courtesy: Oxford University Press
 Courtesy: X / Jaime Kirzner-Roberts
Courtesy: X / Jaime Kirzner-Roberts
Iran’s Jews in the crosshairs
 Courtesy: The Jakarta Post
Courtesy: The Jakarta Post
Bombay to Jakarta via spices, films, people
 Courtesy:
Courtesy:
Bombay-Antwerp: A tale of two port cities
 Courtesy:
Courtesy:
Bombay’s Polish legacy
 Courtesy:
Courtesy:
His Majesty’s Headhunters: The Siege of Kohima that Shaped World History
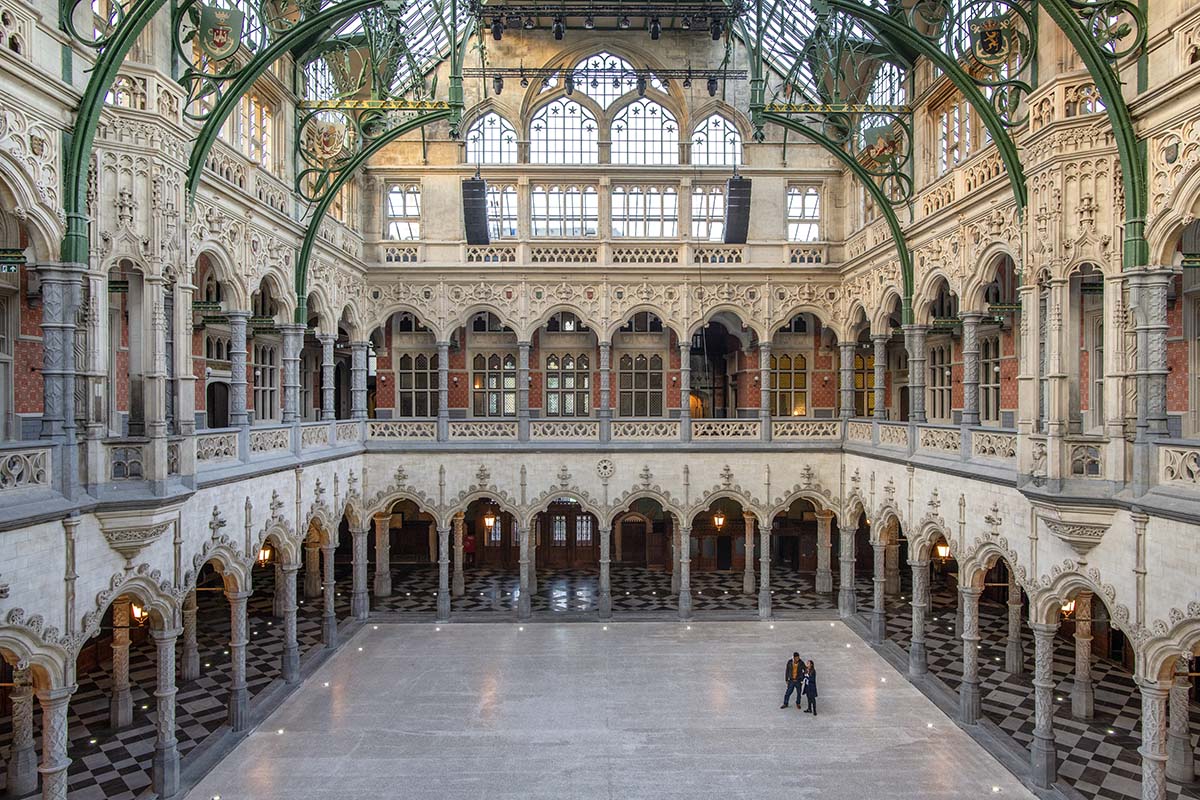 Courtesy:
Courtesy:
The global Indian diamantaire network
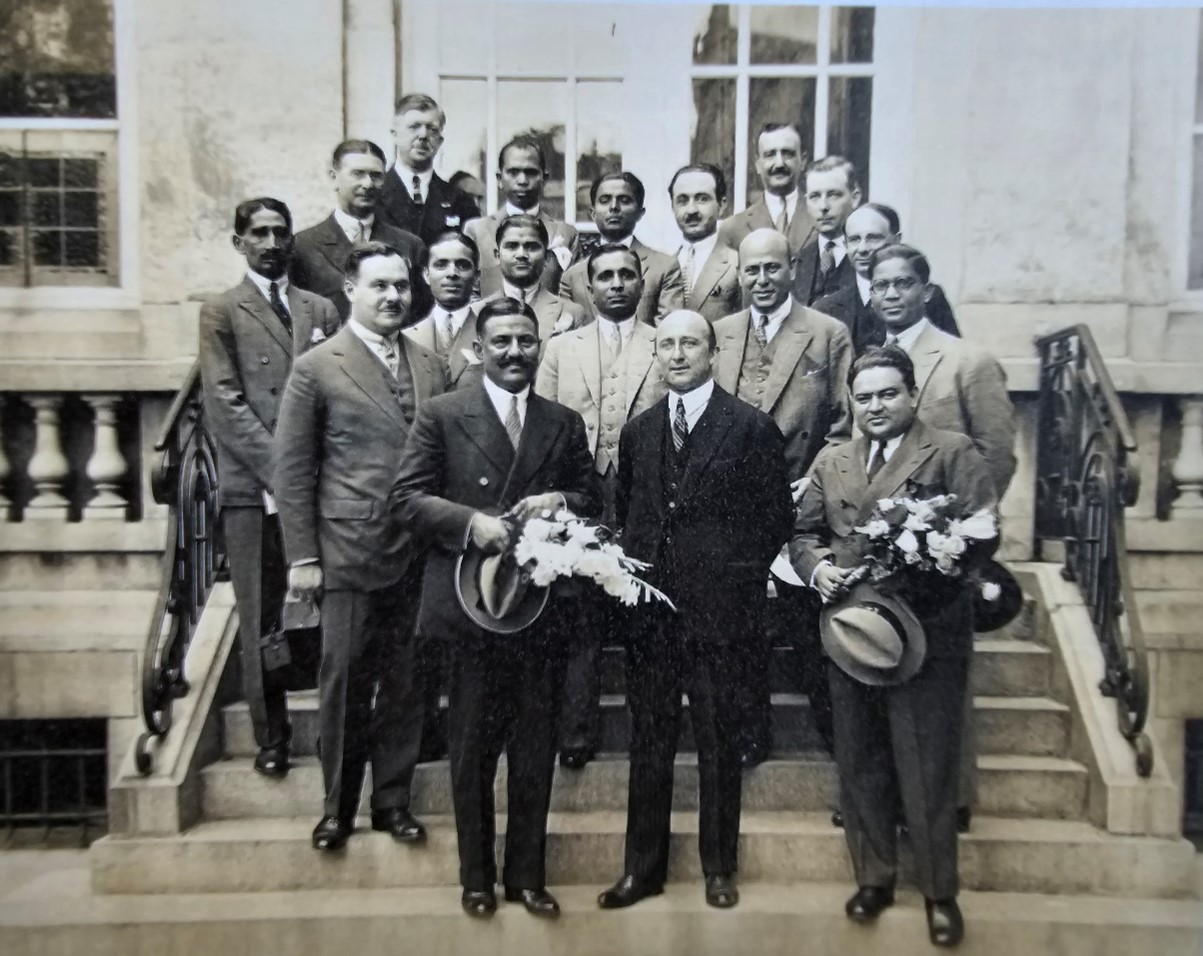 Courtesy: Suresh Mehta and 'Fragrant Folios: The Palanpur Story' by Jitendra C. Mehta and Amrit Gangar.
Courtesy: Suresh Mehta and 'Fragrant Folios: The Palanpur Story' by Jitendra C. Mehta and Amrit Gangar.
A century of Bombay-Antwerp diamond trade
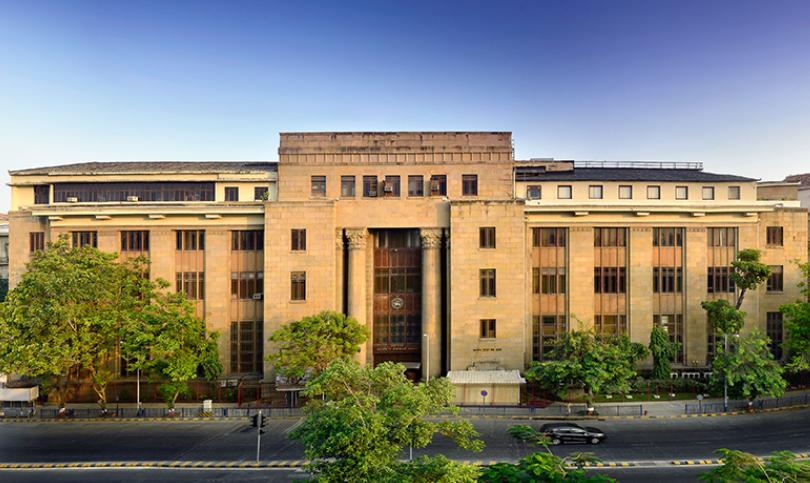 Courtesy: Shapoorji Pallonji
Courtesy: Shapoorji Pallonji
A central bank for India in Bombay
 Courtesy: Sarmaya Arts Foundation
Courtesy: Sarmaya Arts Foundation

