Trump’s Iran sanctions hit India
India may end up being the unintended victim of renewed U.S. sanctions on Iran. It will push up the price of oil and cost India billions of dollars annually
 Courtesy: Gateway House
Courtesy: Gateway House
India may end up being the unintended victim of renewed U.S. sanctions on Iran. It will push up the price of oil and cost India billions of dollars annually
Cyrus Rustomjee, Senior Fellow, Global Economy Program, Centre for International Governance Innovation, Canada, spoke to Gateway House on how the Blue Economy offers exciting opportunities to even the poorest developing countries to eradicate poverty
 Courtesy:
Courtesy:
The removal of 11 top ministers in the Riyadh government last week by the young crown prince Mohammad bin Salman, is a geopolitical upheaval, the implications are serious. Domestically, the kingdom is seeking to liberalise its conservative society and move away from oil-dependency – evident from the expected listing of its crown jewel Aramco. For India, which imports oil largely from West Asia, instability could cause a spike in prices, leaving less for its ambitious reforms. Globally, there is now space for new alignments – in the Great Power plays, in the Shia-Sunni rivalry, and in the war on terrorism.
 Courtesy: New York Times
Courtesy: New York Times
Three epoch-making events in 2016 are continuing to have global repercussions. They were: Brexit, China’s rubbishing of the July verdict of the Permanent Court of Arbitration after it rejected its claims on disputed islands in the South China Sea, and Trump’s election. This article, the prologue to a book-in-progress, The Hinge Year – Geopolitical Dislocations and Dispersals, outlines how these events intersect with transformed geoeconomic realities
 Courtesy: Asharq Al-Awsat
Courtesy: Asharq Al-Awsat
Saudi Arabia and its allies have broken off diplomatic ties with Qatar, but Iran may be their real target, a possibility reinforced by some recently leaked emails from a UAE diplomat
 Courtesy: Wikipedia
Courtesy: Wikipedia
The transition to renewable energy is hampered by the lack of suitable, affordable products and specialised financing for its infrastructure. This infographic, as part of a policy brief put forth by Gateway House, set to be tabled at the 2017 Hamburg G20 conference, outlines an ecosystem to overcome these hurdles
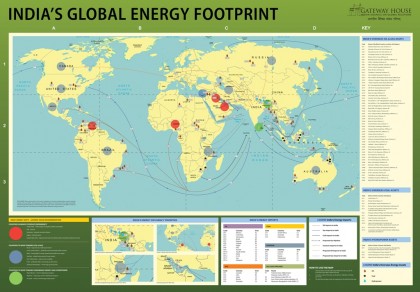 Courtesy: Gateway House
Courtesy: Gateway House
Trends in technology, geopolitics and geoeconomics have dramatically transformed the global energy scenario in the last two years. This means favourable conditions for import-dependent India, which must use the opportunities available to reduce its vulnerability to high energy prices. The jump in oil prices past the $60 mark suggests that India must act with alacrity. India’s Energy Footprint Map offers a profile of India’s global trade and investment in energy, and indicates what India can do to access cheap and reliable supplies
Aleppo is back under the control of the Syrian government, the Russian ambassador to Ankara is assassinated for his country’s role in Syria, and U.S. President-elect Donald Trump wants to cooperate with Russia to fight ISIS in Syria. These momentous events in modern history compel an assessment of the geopolitics surrounding Syria.
 Courtesy: bdnews24
Courtesy: bdnews24
India imports 80% of its oil and 80% of the imports are from vulnerable regions. This high-cost, high-risk approach is not sustainable, and the current low price of oil offers India an opportunity to secure its long-term energy needs by taking three concurrent steps: diversifying supply sources, investing in oil fields, and using financial instruments
 Courtesy: Wikipedia
Courtesy: Wikipedia
The Indian oil industry is changing. The recent bidding for Discovered Small Fields saw the emergence of small, independent oil explorers in a country that has been dominated by state-owned companies and only a few private sector firms