BRI sputters in South Asia
A decade after its launch, China’s Belt and Road Initiative has slowed down in South Asia, the result of poorly conceived projects, and irresponsible behavior from borrower and lender alike.
 Courtesy:
Courtesy:
A decade after its launch, China’s Belt and Road Initiative has slowed down in South Asia, the result of poorly conceived projects, and irresponsible behavior from borrower and lender alike.
 Courtesy: Shutterstock
Courtesy: Shutterstock
Pakistan’s latest economic survey reveals the extent of the country’s indebtedness to China. High-interest Chinese loans, reckless multilateral borrowing, and ever-increasing defence budgets have deleteriously impacted Pakistan’s finances. Any lasting solution to these problems will have to involve China.
 Courtesy: Xinhua
Courtesy: Xinhua
China has followed Sun Tzu’s strategy of focussing on alliances - building its own and weakening those of its adversaries. Beijing’s carefully nurtured formations in West and Central Asia are part of this global power projection, especially with Pakistan, Iran and now, the Taliban, through projects like the Belt and Road Initiative. India must recalibrate its China policy and push for concerted regional responses to emerge as a balancing force against it.
 Courtesy: Gateway House
Courtesy: Gateway House
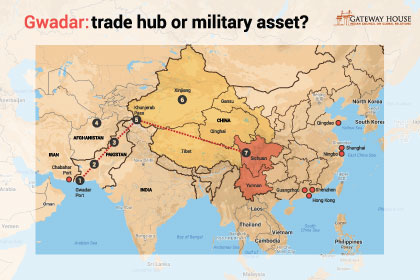
China’s ostensible intentions are to turn Gwadar port into a focal point of the China Pakistan Economic Corridor. But the geography of the region is a major stumbling block in the realisation of these ambitions and raises questions about the project’s underlying motives
 Courtesy: Gateway House
Courtesy: Gateway House
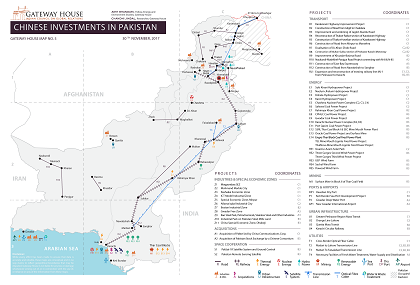
The China-Pakistan Economic Corridor is a strategic play by China disguised as an economic corridor. It may bring some economic benefits to Pakistan in the short run, but will almost certainly cost the country – and India – a big political price in the long run
 Courtesy: AP
Courtesy: AP
India’s new focus on Balochistan has more to do with the China Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC) than with Kashmir. China understands that CPEC may not be achievable. But there are real dangers in reviving Pakistani fears of secessionism and in broadening the field of Indo-Pakistani conflict beyond the confines of Kashmir.