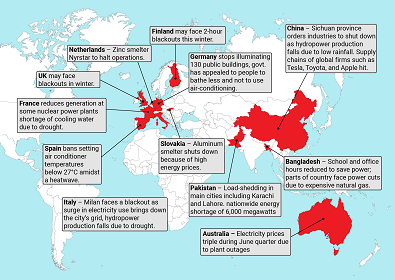
Energy-bereft world in darkness
Sanctions against Russian energy, high cost fuel, heat waves and droughts all at once have raised the price of daily energy use to unprecedented levels and plunged large parts of the world into darkness.
 Courtesy: Getty Images
Courtesy: Getty Images
Sanctions against Russian energy, high cost fuel, heat waves and droughts all at once have raised the price of daily energy use to unprecedented levels and plunged large parts of the world into darkness.
 Courtesy: TIME
Courtesy: TIME
Last month, the Government of India released its Green Hydrogen Policy with the goal of boosting energy self-reliance and inspiring clean energy transitions. The time is right for the Indo-Pacific economies to finance green hydrogen projects and integrate them into supply chains.
 Courtesy: Ministry of External Affairs, Government of India
Courtesy: Ministry of External Affairs, Government of India
Saurabh Kumar, Secretary (East), Ministry of External Affairs, Government of India, delivered the keynote address at the panel discussion on India in the Indo-Pacific: Pursuing Prosperity and Security, organised by Gateway House and the U.S. Embassy, New Delhi, on 1 February 2022. He outlined India's vision for a free and inclusive Indo-Pacific, and the initiatives undertaken to further cooperation among nations in the region.
 Courtesy: Shutterstock
Courtesy: Shutterstock
Since August 2021, Western Europe has faced a problem with renewable energy, causing it to turn to natural gas as an emergency alternative. This has led to a significant increase in gas prices and has serious implications for fertiliser and food prices. If this trend continues, it will be likely to cause food insecurity especially in poorer nations which do not have the monetary cushion of the West.
 Courtesy: CNBC-TV18 (Youtube)
Courtesy: CNBC-TV18 (Youtube)
On 30 July 2021, Lisa Curtis and Surjit Bhalla, co-chairs of the Gateway House Quad Economy and Technology Task Force, spoke to CNBC-TV-18 on the various channels of cooperation between the Quad countries in technology, supply chains and undersea cables, and the need to counter China's dominance in the Indo-Pacific.
 Courtesy: Shutterstock
Courtesy: Shutterstock
India’s oil consumption and imports are likely to resume their upward trajectory as the economy opens up, after a temporary drop due to the pandemic. To secure its energy needs, the country should shift course from investing in oil and gas assets of emerging economies to those of developed nations. The oil-rich Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) countries, such as Canada, Norway, and the U.S. can be given special consideration.
 Courtesy: Gateway House
Courtesy: Gateway House
India’s investments in energy thus far have concentrated on buying stakes in oilfields in developing countries often at the risk of political unpredictability. With oil prices, and therefore oil company values, falling – India should revise this strategy and aim for better value and lower risk by making investments in companies in the developed world. This paper recommends investing in oil and gas assets in energy-rich developed countries like the U.S., Canada and Australia, to reduce India's vulnerability to future increases in energy prices. These should be made via a sovereign wealth fund (SWF), not the national oil companies. The SWF will be best served by acting as a financial investor, acquiring, only minority stakes, rather than aiming for management control.
 Courtesy: Gateway House
Courtesy: Gateway House
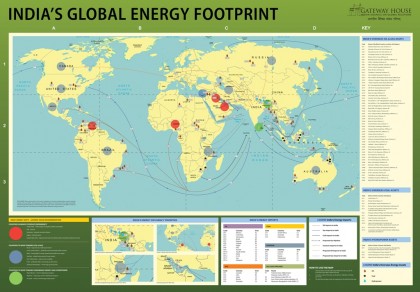
Trends in technology, geopolitics and geoeconomics have dramatically transformed the global energy scenario in the last two years. This means favourable conditions for import-dependent India, which must use the opportunities available to reduce its vulnerability to high energy prices. The jump in oil prices past the $60 mark suggests that India must act with alacrity. India’s Energy Footprint Map offers a profile of India’s global trade and investment in energy, and indicates what India can do to access cheap and reliable supplies
 Courtesy: pmindia.nic.in
Courtesy: pmindia.nic.in
The India-Australia civil nuclear deal goes much beyond providing for India’s energy needs. The deal will help New Delhi’s bid to enter the Nuclear Suppliers Group and other technology control regimes. The ties with Canberra also have the potential to develop into a strong strategic partnership