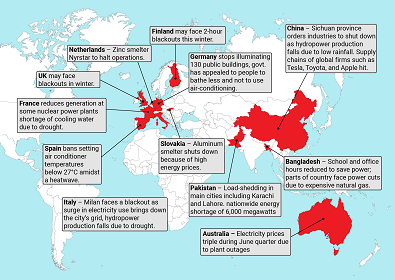
Energy-bereft world in darkness
Sanctions against Russian energy, high cost fuel, heat waves and droughts all at once have raised the price of daily energy use to unprecedented levels and plunged large parts of the world into darkness.
 Courtesy: Getty Images
Courtesy: Getty Images
Sanctions against Russian energy, high cost fuel, heat waves and droughts all at once have raised the price of daily energy use to unprecedented levels and plunged large parts of the world into darkness.
 Courtesy: Shutterstock
Courtesy: Shutterstock
The United Nations’ Paris Agreement of 2015 had nations committing to reduce emissions of greenhouse gases to slow the rise in global temperatures. But terrestrial geoengineering – or the use of “carbon capture” technologies and developing carbon sinks to remove gases already in the atmosphere – and atmospheric climate engineering are technologies which also seek to slow global warming
 Courtesy: thinkprogress.org
Courtesy: thinkprogress.org
Earth Day, which fell on April 22, is an apt time to take stock of carbon emissions. This infographic offers a comparative look at two countries and what their carbon emissions convey about their approach to carbon mitigation
 Courtesy: ibctrain.com
Courtesy: ibctrain.com
The main objective of the Shanghai Cooperation Organisation’s (SCO) Energy Club, when Russia formed it, was to market its member states’ substantial oil and natural gas reserves. This map shows some of the important natural gas pipelines, originating from Russia and its neighbouring countries that are not members of the SCO. What can India do to secure supplies from these abundant but currently inaccessible natural gas reserves?
 Courtesy: Gateway House
Courtesy: Gateway House
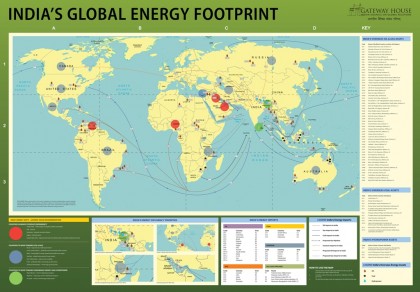
Trends in technology, geopolitics and geoeconomics have dramatically transformed the global energy scenario in the last two years. This means favourable conditions for import-dependent India, which must use the opportunities available to reduce its vulnerability to high energy prices. The jump in oil prices past the $60 mark suggests that India must act with alacrity. India’s Energy Footprint Map offers a profile of India’s global trade and investment in energy, and indicates what India can do to access cheap and reliable supplies