India’s Strategic Imperative in the South Pacific
This report analyses the significance of expanding India’s engagement with the South Pacific in the backdrop of mounting global interest in the region
 Courtesy: Madhu Amodia
Courtesy: Madhu Amodia
This report analyses the significance of expanding India’s engagement with the South Pacific in the backdrop of mounting global interest in the region
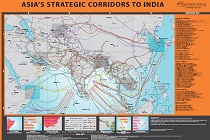 Courtesy: Gateway House
Courtesy: Gateway House
The map – Asia’s Strategic Corridors to India – has emerged from Gateway House’s study of India’s strategic links with other parts of Asia. It highlights the progress India has made in forging multiple links with six strategic regions – Central Asia, West Asia, East Africa, South-East Asia, East Asia, and our immediate neighbourhood
 Courtesy: Australian Government Department of Defence
Courtesy: Australian Government Department of Defence
Defence Minister A. K. Antony’s visit to Australia this week was a significant step forward in the defence relationship. In coming years an India-Australia partnership will be important for managing maritime security in the Indian Ocean and will also have implications for security in Southeast Asia and the Pacific
 Courtesy: Jessica Taekman/Flickr
Courtesy: Jessica Taekman/Flickr
Indian Prime Minister Manmohan Singh and Japan’s Shinzo Abe are giving heft to a renewed partnership and a focus on the Indo-Pacific. Both nations must collaborate and work with South Pacific countries, especially Tonga, to counter China’s growing influence in this increasingly geopolitically important region
 Courtesy: U.S.Navy Imagery/Flickr
Courtesy: U.S.Navy Imagery/Flickr
An understanding between China and India not to develop a permanent presence on each other’s maritime territories may be helpful in reducing tensions between the two navies. Given the broader context of Sino-Indian strategic rivalry, however, this seems unlikely.
 Courtesy: Furmeyer/WikimediaCommons
Courtesy: Furmeyer/WikimediaCommons
Maritime piracy is one of the several grave security issues faced by today’s world. This problem, however, isn’t a new phenomenon, and nations have long-battled this issue. How did piracy manifest itself in the Indian Ocean in the 19th century, and what was the nature of counter-piracy efforts during that period?
 Courtesy: mpeacey/Flickr
Courtesy: mpeacey/Flickr
Traditionally, the South Pacific islands have been considered strategically insignificant. However, the need for resources, and the geopolitical shift towards Asia-Pacific have prompted nations to realize that these small island states control large resource-rich ocean areas and are increasingly geostrategic.
 Courtesy: Columbia/WikimediaCommons
Courtesy: Columbia/WikimediaCommons
In the 1700s, one man antagonized the European powers, and insisted on the Maratha Empire’s rights to taxation and sovereignty over Maharashtra’s coast. He was Kanhoji Angre, the head of the Maratha navy. How did he, 283 years ago, set an important precedent for the Subcontinent’s local powers?
 Courtesy: BlatantWorld.com/Flickr
Courtesy: BlatantWorld.com/Flickr
The concern with piracy is in our waters is three-fold: the threat to Indian-owned vessels and Indian citizens; the difficulty in dealing with piracy and hostage-taking on the high seas; and finally, squeezing the organized industry. Can India play a leadership role in this effort?
Gateway House’s Alisha Pinto interviews former Somali Ambassador to India, Mohammad Osman Omar, on piracy issues and maritime security from the coast of Somalia to the waters of the Indian Ocean.