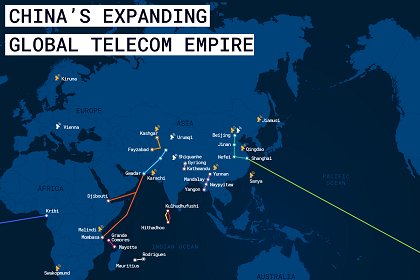
Version 2: Mapping China’s global telecom empire
This version of the Gateway House Map on China’s Expanding Global Telecom Empire identifies some more telecommunication assets -- optic-fibre and satellite ground stations -- that Beijing is working on in South and Central America, Africa, Myanmar, the Indian Ocean Region and mainland China besides the existing ones, such as the Pakistan East Africa Cable Express (PEACE). It shows the direction China’s investment is taking, its diplomatic overtures and the larger geopolitical implications of its growing telecom empire