India’s long term relations with South Africa
TIMES NOW & Maroof Raza featured our Distinguished Fellow in Foreign Policy Studies, Amb. Rajiv Bhatia on their show to discuss long-term India-South Africa ties. Watch the full episode here.
 Courtesy:
Courtesy:
TIMES NOW & Maroof Raza featured our Distinguished Fellow in Foreign Policy Studies, Amb. Rajiv Bhatia on their show to discuss long-term India-South Africa ties. Watch the full episode here.
 Courtesy:
Courtesy:
BRICS has grown in influence in its first decade but is still far from achieving its initial goals
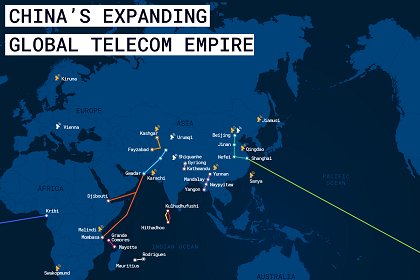 Courtesy: Gateway House
Courtesy: Gateway House
This version of the Gateway House Map on China’s Expanding Global Telecom Empire identifies some more telecommunication assets -- optic-fibre and satellite ground stations -- that Beijing is working on in South and Central America, Africa, Myanmar, the Indian Ocean Region and mainland China besides the existing ones, such as the Pakistan East Africa Cable Express (PEACE). It shows the direction China’s investment is taking, its diplomatic overtures and the larger geopolitical implications of its growing telecom empire
 Courtesy:
Courtesy:
Our Distinguished Fellow in Foreign Policy Studies, Amb. Rajiv Bhatia, was interviewed by the Economic Times analysing the visits of Chinese Premier Xi Jingping and Indian PM Narendra Modi to Africa ahead of the BRICS Summit. Read the full article Read more
 Courtesy: Tide of Fortune: A family tale, by Manubhai Madhvani
Courtesy: Tide of Fortune: A family tale, by Manubhai Madhvani
Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s visit to Rwanda and Uganda, en route to the BRICS Conference in South Africa (July 25-27), is significant as it is a rebolstering of ties with these East African landlocked nations through their Indian diasporas, ties that will be cemented further by cooperation in defence, finance, education and other sectors. The Bombay Presidency once played a key role in the development of this region
 Courtesy:
Courtesy:
An article written by our Distinguished Fellow in Foreign Policy Studies, Amb. Rajiv Bhatia, was quoted in a print article by China Global Television Network (CGTN) on PM Modi’s upcoming visit to Africa. Read the full article here.
 Courtesy: Kremlin website
Courtesy: Kremlin website
The annual diplomatic exercise next week takes place amid a complex global political scenario. The western alliance is deeply divided, Brexit is near and equations among the great powers are in a constant state of flux. BRICS may now do well to focus more on internal cooperation than global change
 Courtesy: Sfgate.com
Courtesy: Sfgate.com
The governments of India and South Africa are eager to reinvigorate their relationship after it suffered damage in the latter half of Jacob Zuma’s presidency. The current president has spoken of a ‘new dawn’ for his country, driven by economic advancement. In that, India can play a big role
 Courtesy: GovernmentZA/ Flickr
Courtesy: GovernmentZA/ Flickr
China’s judicious deployment of economic diplomacy—in sectors ranging from infrastructure and agriculture to skill development--has enabled it to develop relations with several African countries. India, Africa’s oldest partner, which is diversifying its own relationship, can replicate parts of China’s approach
 Courtesy: Exim Bank of India
Courtesy: Exim Bank of India
The India-Africa economic partnership lags some way behind the diplomatic reciprocity the two countries share. Africa has had a trade surplus with India in the past decade, but increasing two-way trade of goods and services across sectors calls for serious promotional measures and removal of non-tariff barriers. The government, Indian business and their African partners need to devise an action plan that can take trade to $100 billion and investment to $75 billion by 2022